Keeping track of your blood sugar (glucose) levels is one of the most important steps in maintaining good health—especially if you're living with diabetes or at risk of it. Understanding what blood sugar levels mean, what’s considered normal, and how to interpret the numbers can help you make informed lifestyle and health decisions.
What Is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar is the amount of glucose present in your blood. Glucose is your body’s main source of energy and comes from the food you eat, especially carbohydrates. After you eat, your blood sugar rises and then drops as insulin (a hormone made by the pancreas) helps your cells absorb the sugar.
If your body doesn't use insulin properly or doesn't make enough of it, blood sugar can remain high—leading to conditions like pre-diabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Why Monitoring Blood Sugar Matters
Checking your blood sugar levels regularly helps:
- Detect early signs of diabetes
- Manage existing diabetes effectively
- Prevent complications like nerve damage, heart disease, and kidney issues
- Understand how food, stress, exercise, and medication affect your glucose levels
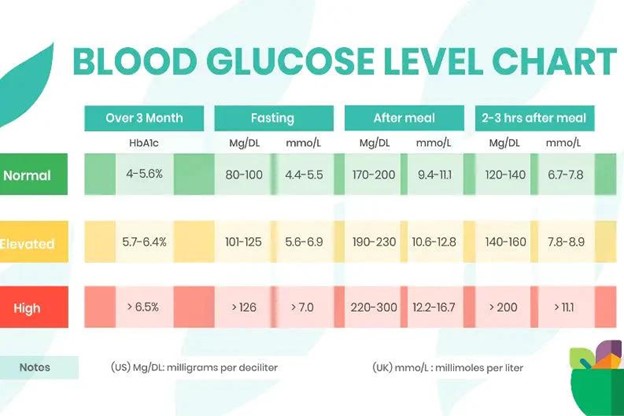
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Here’s a simple chart to help you understand what blood sugar levels typically look like:
| Condition | Fasting (before meals) | 2 Hours After Meals |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 70–99 mg/dL | Less than 140 mg/dL |
| Pre-diabetes | 100–125 mg/dL | 140–199 mg/dL |
| Diabetes (Type 2) | 126 mg/dL or higher | 200 mg/dL or higher |
Note: These values are general guidelines. Always consult your doctor for personalized ranges.
Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia):
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia):
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Irritability
Both extremes need attention. If left untreated, they can lead to serious complications.
Tips to Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
- Eat balanced meals: Include high-fiber vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Avoid processed sugar and refined carbs.
- Exercise regularly: Even a 30-minute walk daily can help regulate blood sugar.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support kidney function and flush out excess sugar.
- Manage stress: High stress can spike blood sugar. Try yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Get regular checkups: Your doctor may recommend blood tests like HbA1c to monitor long-term glucose control.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice symptoms of abnormal blood sugar or consistently get unusual readings, consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve your quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your blood sugar levels isn’t just for people with diabetes—it’s something everyone can benefit from. With the right knowledge, diet, and habits, managing your glucose levels can become second nature.
visit now : normal-blood-sugar-levels-chart
Keep this chart handy, listen to your body, and stay proactive about your health!